Total orange production for the 2023-2024 crop season ended at 307.22 million boxes1
The 2023-2024 orange crop for the São Paulo and West-Southwest Minas Gerais citrus belt, published by Fundecitrus – performed in cooperation with Markestrat and full professors from FEA- RP/USP and FCAV/Unesp2 – concluded with 307.22 million boxes of 40.8 kg each (90 lbs), divided as follows:
- 58.09 million boxes of the Hamlin, Westin and Rubi early-season varieties;
- 18.51 million boxes of the Valencia Americana, Seleta, Pineapple and Alvorada early-season varieties;
- 97.62 million boxes of the Pera Rio mid-season variety;
- 105.20 million boxes of the Valencia and Valencia Folha Murcha late-season varieties;
- 27.80 million boxes of the Natal late-season variety.
Of the total, about 27.82 million boxes were produced in the Triângulo Mineiro region.
The season´s production was 2.22% lower in comparison to the previous crop, which reached 314.21 million boxes and was 0.69% below the initial forecast made in May 2023 …
Please download the complete forecast under: www.fundecitrus.com.br/pdf
1Hamlin, Westin, Rubi, Valencia Americana, Seleta, Pineapple, Alvorada, Pera Rio, Valencia, Valencia Folha Murcha, and, Natal.
2Department of math and science, FCAV/Unesp Jaboticabal Campus.
A survey carried out through independent auditing of each of the companies associated with CitrusBR and also consolidated by external auditing revealed that the total oranges processed in the Sao Paulo and Minas Gerais Citrus Belt in the 2022/23 season was estimated at 265,292,217 boxes of oranges of 40.8 kg of which 243,967,550 boxes were processed by CitrusBR members and close to 21.3 million boxes were processed by non-members.
With the final estimated juice yield on fruit of 280.58 boxes of oranges to produce one metric ton of FCOJ equivalent in aggregate for CitrusBR members and non-members, the final estimate for total orange juice production for the 2022/23 season was of 945,529 metric tons of FCOJ equivalent …
Please download the full report: www.citrusbr.com
The orange output in the citrus belt in southeastern Brazil (São Paulo and the Triângulo Mineiro) in the 2023/24 season is estimated at 309.34 million boxes of 40.8 kg each, according to data from Fundecitrus (Citrus Defense Fund) released on May 10th. This volume is 1.5 % lower than that harvested last season.
According to Fundecitrus, the major reasons for the lower harvest are rains above the historical average (although they have favoured both the vigor of trees and fruits growth, rains raised flower rotten), the negative biennial cycle (except for northern SP, where productivity was lower last season), lower blooming for some late varieties (whose harvesting was delayed and/or production was high in 2022/23) and the higher incidence of greening, which is expected to raise the rate of fruit fall. On the other hand, high moisture may favour fruits weight, which may be the highest since 2017/18.
As for productivity, the average forecast for the citrus belt is at 918 boxes per hectare, a slight 0.6 % up from that in the 2022/23 season.
Although the harvest expected in the citrus belt is within the average of the last 10 years, the needs of juice processors in SP for oranges is very high. Inventories are low, and the number of oranges to be available is not expected to be enough for stocks to recover.
Indeed, according to a report from CitrusBR released this month, the volume of juice stocked by the processors in SP in Dec/22 was 14.5 % lower than that in the same period of 2021. If this percentage continues stable until the end of the 2022/23 season (on June 30, 2023), ending stocks may total 122.3 thousand tons (juice equivalent), very low – maybe even insufficient – to meet the markets’ demand until the new season steps up.
Flowers of the 2023/24 crop, verified in the second semester of 2022, were considered excellent in the citrus belt of São Paulo and Triângulo Mineiro, which resulted in expectations of a good harvest. However, the weather after flowers blossomed was not ideal in many areas. Therefore, the next season may register lower supply compared to the demand.
Areas that have irrigation system (44 % of the total is located in the north of São Paulo state) registered anticipated flowers (in mid-July), and the weather was good after the blossoming. In this case, the development is considered satisfactory.
In other areas, however, scenarios were very distinct, since the rainfall was irregular and at different volumes among the regions. In the southwest of SP, flowers blossomed in late September, while it occurred in mid-October in other areas. In this case, as flowers opened in the rainy season (September/October), there had been more cases of blossom-end rot (“estrelinha”), increasing flower abortion.
Another aspect that reinforced concerns of the citrus sector in Brazil is the below-average amount of rainfall in many regions during the flower-settlement (especially in November), and temperatures were high in some moments. Thus, fruitlets dropped. From mid-December until now, rains have been more frequent, which brings relief, but are not capable to revert the scenario of losses.
In general, players expected that the 2023/24 season would be higher than the current; however, after many difficulties, opinions have started to change. The USDA released a report in December indicating that the Brazilian production may total 305 million 40.8-kilo boxes, 1.9% less compared to the current crop. It is important to mention that a more accurate forecast for 2023/24 will be possible only in mid-February.
Therefore, the scenario of low inventories at the end of 2022/23 may not be reverted in the next season. CitrusBR says that the ending stocks by June/23 may total only 140 thousand tons, lower than the strategic level, of 250 thousand tons.
Cepea calculations indicate that, in order for the volume in stocks by the end of 2023/24 (in June/24) returns to the strategic level of 250 thousand tons, the orange processing in 2023/24 may be at roughly 300 million 40.8-kilo boxes, which is equivalent to a production in São Paulo state and in Triângulo Mineiro at 340 million boxes, higher than what the USDA forecast.
TAHITI LIME – The first two months of 2023 may register high supply in São Paulo state, due to the peak period, which can press down quotations. On the other hand, as the industry may intensify processing activities and exports tend to increase in this period, the volume available is expected to reduce in the domestic market.
The Brazilian exports of orange juice increased in the first months of the 2022/23 season (July and August 2022). According to data from Secex, Brazil exported 175.9 thousand tons of Frozen Concentrate Orange Juice (FCOJ) Equivalent in July/August, 8 % more than that in the same period last year. Revenue totaled USD 332.6 million, 32 % up in the same comparison.
The exports of non-concentrate juice (NCJ) have had the highest increase this season, totaling almost 292.7 thousand tons, with a revenue of USD 108.3 million, 14 % and 24 % up from that in July/August last year. On the other hand, the revenue from FCOJ exports rose higher than that for NCJ, by 36 %, totaling USD 224.3 million in the first two months of the current crop; the volume shipped increased by 6 %, totaling 122.7 thousand tons.
These increases were already expected for this season, considering that, in 2021/22, the Brazilian exports were limited by estimates for low stocks of orange juice.
In August, CitrusBR reported that, in June/22, only 143 thousand tons of FCOJ were stocked, a steep 55 % down from that in June/21. CitrusBR considered a possible increase in the exports to the USA because of the low orange production in Florida, due to the high incidence of greening.
DESTINATIONS – The European Union continues as the number one destination for the Brazilian orange juice, with a share of 62 % in the total exported – in the same period last season, its share was at 64 %. The second major destination for the national juice is the United States, with a share of 21 % in the total, against 25 % in 2021. The share of other destinations increased from 12 % last season to 17 % this season (considering the months of July and August).
South-Central Florida experienced a bout of extremely cold weather during the last few days of January, resulting in frost and icing throughout many Floridian orange groves. In the immediate aftermath of this event, farmers initially reported that the damage to their groves was minimal. However, more recent estimations paint a clearer picture of the frost’s effects, with certain grove locations recording temperatures as low as ~20 degrees Fahrenheit lasting for upwards of two days. Such sustained conditions of frost have not been observed in Florida for over five years. Temperatures below 30 degrees often lead to bloom damage on citrus trees, which can drastically affect the quality of their subsequent harvests.
Fruit droppage rates also appear to be a major issue for many Florida citrus growers post-freeze. As temperatures drop for sustained periods of time, the juices contained within citrus fruits become frozen, resulting in premature fruits dropping from their branches. This can happen in as little as 6 hours after exposure to substantial freezing temperatures; Florida’s freeze lasted for two days. As such, it will be difficult for farmers to fully assess the damage dealt to their groves until temperatures warm up to regularity once again. Other conditions expected to affect citrus trees in the region are wood injury and external fruit damage, both of which will reduce harvest levels.
Florida has already weathered a challenging orange season up to this point, with fruit estimates falling from 47 million boxes to just 44.5 million midway through January. These shifting numbers represented a 13 % reduction in harvest size when compared to Florida’s previous orange season, and it seems as though the difference between the two will only continue to grow from the effects of the freeze.
The global orange market is quite volatile currently, with prices rising on a regular basis due to an ongoing drought in Mexico and a difficult growing season for Brazil (frost has also been an issue there). As such, it seems likely that orange oil and its derivatives will continue to rise in price as availability of new materials reduces.
Orange1 production forecast update totals 267.87 million boxes
The first 2021-2022 orange crop forecast update for the Sao Paulo and West-Southwest Minas Gerais citrus belt by Fundecitrus – performed in cooperation with Markestrat, FEA-RP/USP and FCAV/Unesp2 – is 267.87 million boxes of 40.8 kg each, differently from the 294.17 million estimated in May this year. The reduction of 26.30 million in relation to the initial expectation corresponds to – 8.9 %. The main reason for this crop loss is the poorer rainfall regime constituting the most severe water crisis ever to hit Brazil for the last 91 years3. The combination of this drought never before experienced by citriculture and successive frosts in July culminated in a gradual crop decline that has been seen as harvests progress and disclose totally atypical figures. Field surveys also show results other than expected for this time of the year for orange planted areas yet to be harvested. In general, oranges are excessively small, and early fruit drop reaches one of its highest rates. These factors make production go back to the same levels of last crop season that totaled 268.63 million boxes, despite fruit load being 12.50 % larger since this is an “on” year. In view of this data and the perspective of climate conditions remaining adverse until harvests end, fruit should present the most critical size and drop rate in historical data. If this scenario is confirmed, there will no longer be an increase in this crop in relation to the previous season, estimated at 9.51 % in May, but rather a smaller volume than the production in the last season (- 0,28 %). …
1Hamlin, Westin, Rubi, Valencia Americana, Seleta, Pineapple, Pera Rio, Valencia, Valencia Folha Murcha and Natal.
2Department of math and science, FCAV/Unesp Jaboticabal Campus.
3National operator of the energy system – ONS. Data for the Parana River basin, encompassing the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, Paraná, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul, Mato Grosso do Sul, Goiás and Distrito Federal.
Please download the complete forecast under: www.fundecitrus.com.br/pdf
On 12 May 2021, the World Citrus Organisation celebrated its first Annual Meeting online, following the official creation of the organisation last year. During the AGM, the WCO Secretariat presented the consolidation of the production and export forecasts for the forthcoming Southern Hemisphere citrus season 2021. This preliminary forecast is collected from member industry associations in Argentina, Australia, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Peru, South Africa, and Uruguay.
The WCO held its Annual meeting ending a first year of activities. The Co-chairs of the association, Jose Antonio Garcia (Ailimpo) and Justin Chadwick (CGA) agreed to state: “The full first year of operation allowed the organisation to quickly build a representative association and provide the benefits and value to the members”.
During the meeting, the preliminary forecast presented shows that the 2021 citrus Southern Hemisphere crops is expected to reach 22.7 million tons, which represents an increase of 3.18 % compared to the 2020 crop. Export is expected to increase by 12.72 % to 3.8 million tons. Philippe Binard, Secretary General of WCO stated while presenting the data : “following the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, a positive trend of consumers’ demand for fruit and veg. was noted, in particular for citrus fruit, widely recognised for its high nutritional value, notably in terms of vitamin C content. The large volume available is positive news as it will meet the increased demand”. On the processing side, a total of 13.4 million tonnes of citrus are expected to be destined to the juice market, which constitutes a slight increase of 1.26 % compared to the previous year. It is however worth noting that Brazil’s data provided for the forecast remains preliminary, with the official Brazilian data expected to be confirmed in the coming weeks.
By citrus categories, the soft citrus showed the greatest increase in production, by 10.57 %, with a significant increase in export volumes of over 20 % to 1 million tonnes of export. Orange production remained broadly stable (+ 1.93 %), whilst lemon (+ 2.37 %) and grapefruit (+ 6.44 %) showed greater increases. Exports are also expected to increase for all varieties, orange (+ 11.55 %), lemon (+ 7.20 %) and grapefruit (+ 9.56 %). Eric Imbert (CIRAD- Technical Secretariat of WCO) indicated: “The Southern Hemisphere citrus export continues to grow in particular for lemons and easy peelers. The Southern Hemisphere today represents 27 % of the global citrus market.” During WCO’s AGM, members also reviewed the past season’s results with a focus on the impact of the covid pandemic, and analysed the estimations for the current season.
In addition, during the meeting, Natalia Santos, Deputy Secretary General of WCO announced that: “Members decided to set-up a formal working group on health & nutrition. This will enable better knowledge- exchange among members on citrus nutritional assets and will also contribute towards a better understanding of the health attributes of citrus. The first meeting of WCO’s Health & Nutrition focus group will take place in the second semester of 2021”, she added.
In general, citrus prices were high in São Paulo State in 2020. With the lower orange production in the Brazilian citrus belt (São Paulo and the Triângulo Mineiro) in the 2020/21 season due to bad weather conditions, the demand from processors for fruits continued high along the year, which underpinned prices.
According to a report released by Fundecitrus on December 10, crop failure in the citrus belt (SP and the Triângulo Mineiro) should be the worst since 1988/1989, when the series began. In total, orange production should be 30 % lower in the 2020/21 season, totaling 269.36 million boxes of 40.8 kilos each.
INDUSTRIAL PRICES – Although processors began the 2020/21 season with high volumes of juice stocked – 471 thousand tons of Frozen Concentrate Orange Juice (FCOJ) Equivalent, according to CitrusBR –, low orange supply kept the demand for fruits high, which reflects on bidding prices.
On the average of the 2020/21 season, prices in the spot market between July and November closed at 23.51 BRL/box, 17.8 % up from that in the same period of 2019 and 7 % above that in the same period of 2018, in nominal terms.
IN NATURA MARKET – Higher demand from the industry lowered the availability of fruits in the in natura market, since some farmers who usually sell to the in natura market preferred to allocate their fruits to processors, due to the uncertainties caused by the covid-19 pandemic and the attractive prices bid by processors. This scenario added to the weather issues and high demand pushed up orange prices (in natura) all the year. For the variety pera rio, prices hit the highest level of the year in November, when the average was 43.35 BRL/box, on tree, 54.6 % up from that in Nov/19, in nominal terms.
There is a saying among those who have been in the industry for a long time: “there is no harvest like the other”. The current one is overcoming itself; such are the difficulties faced.
The first signs that the season would be different were given by last year’s bloom. Blooming in August and September 2019 was very good. However, a period with no rain in the following months accompanied by intense heat has caused an expressive fruitlet fall. The fruits developed until a 2-3 cm diameter size but were overturned by excessive heat. Rains came up in the end of October and a new flowering is expected.
The harvest season was preceded by the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic. The great demand for labor, much of it coming from northeastern states in the country, concerned everyone and made us take extraordinary care to preserve the health of workers involved in the harvest and of other collaborators from other sectors of the properties.
Thus, the current harvest has been one of great surprises and has presented unusual challenges to citrus growers of the Brazilian citrus belt. The main consequences are presented below.
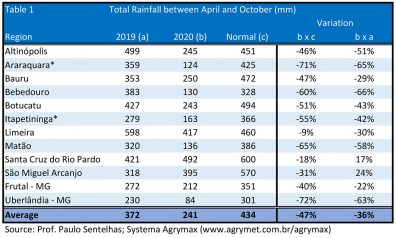
The period without rain, from May of this year until this last month of October, was one of the most extensive ever recorded in the state of São Paulo, according to the graphs and tables below. In addition to drought, very high maximum temperatures were recorded, even at night, causing considerable weight loss and lower fruit quality. The water deficit was very significant in all regions. This is the main reason for the significant decrease in the volume of fruit produced in the “citrus belt”. The losses are more accentuated in the north of the state of São Paulo and in the Triângulo Mineiro, warmer and drier regions.
- However, even further south in the state, losses were above normal. The first harvest estimate released by Fundecitrus, last May, brought an amount of 287.8 million boxes, 25% less than the previous harvest (2019/2020). What you see in the field is a volume of oranges quite below that number. The common perception among consulted technicians and citrus growers is that the final figure is expected to be below 250 million, perhaps below that.
- The period without rain and with temperatures well above the average resulted in extremely withered orchards – plants even died in orchards without irrigation. Another aggravating factor this year was the scarcity of water for irrigation. There are properties that have an installed irrigation structure; however, they do not have enough water available to meet the needs of the plants.
 Due to the flowering in non-traditional months (December and January) there are a large number of “green”, not yet ripe fruits mixed with ripe fruits from the normal flowering (August-September 2019). This brings an additional difficulty to the harvesting operation that has to be carried out in at least two different times, resulting in an increase of the production cost for the citrus growers.
Due to the flowering in non-traditional months (December and January) there are a large number of “green”, not yet ripe fruits mixed with ripe fruits from the normal flowering (August-September 2019). This brings an additional difficulty to the harvesting operation that has to be carried out in at least two different times, resulting in an increase of the production cost for the citrus growers.- This mix of fruits with different level of ripeness, impair the quality of the juices, especially due to the greater amount of limonin present in the green peels of oranges. On the other hand, in the northern regions of the citrus belt, the fruits are getting ripe much faster than normal, producing juices with a ratio (ratio between the amount of sugars divided to acidity) much higher than the average for the period of the year. Industrial income has been better this year than in the previous two years, at least until this time of the harvest (November 2020).
- As a further consequence of this year’s climate events, we will see an increase in the effects of HLB or greening. The symptoms of the disease, such as early fruit fall and low production, usually express themselves more strongly when there is a water deficit. In addition, the psilideo, vector of the disease, presented very high rates even in winter, indicating that we will have a greater number of infected plants in the next years. This has probably occurred because of the warmer climate which resulted in a very irregular or uneven plant vegetation.
What can we expect from the next crop?
The northernmost regions only flourished after the rains that fell in the last days of October. This late blooming should not have a good fruit set because they will be still small in the higher summer temperatures. Moreover, the loss of leaves was very great in the recent drought period, and this will not allow for a large amount of fruit for the next season, since the plant will not be able to provide the metabolites necessary for an expressive fruit set. A good 21/22 harvest is not to be expected for these regions.
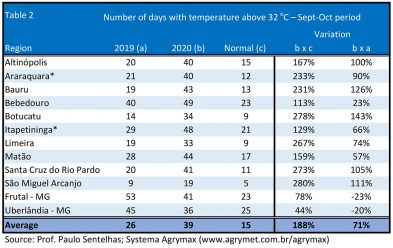
In the most southern regions, which suffered less from water deficit, the flowering came in the normal period, between August and September. However, irregular rainfall and high winter temperatures (table 2), after flowering, have worried producers. What they see in their orchards does not indicate a good harvest for the second year in a row. My experience shows that the harvest after a year as irregular as this one is also not usually good.
Price of juice should go up
Although it is common for citrus to have alternate crops, i.e., smaller crops followed by larger crops, the climatic factors presented in this article should result in two “small” crops in a row, the current and the next seasons.
Thus, Brazilian orange juice industries should process fewer oranges for two consecutive years. This reduction in supply, combined with the growing demand for juices in times of pandemic, should cause increases in the price of juices on the international market.
Author:
Mauricio Mendes
Citrus Consultant
Agriplanning Brazilian Agribusiness Company
GCONCI (Citrus Consultant Group)
Mauricio Mendes is a citrus consultant sine 1980 and Citrus grower since 1988. Has worked to major Citrus Farms in Brazil. Is COO of a 6.000 ha Citrus Farms operation in the SW od Sao Paulo State. Mauricio is also Beachead Advisor for New Zealand Trade and Enterprise (NZTE) . Also has been partner and CEO, for 14 years, of Informa FNP which is one of the most important Agribusiness consultant company in Brazil. FNP was recently acquired by IHS Markit.
Mauricio is also member of GCONCI (Citrus Farming Consultants Group) which gathers 17 Consultants. GCONCI provide direct technical assistance to over 40 million citrus plants (25 % of the Brazilian Citrus Belt)
*Araraquara and Itapetininga are major production citrus regions in São Paulo State.
The WCO Secretariat has released its first crop production forecast for the forthcoming Northern Hemisphere citrus season 2020-21. The preliminary forecast is collected from industry associations in Egypt, Greece, Israel, Italy, Morocco, Spain, Tunisia, Turkey and the United States (California and Florida).
The preliminary forecast shows that the 2020-21 citrus Northern Hemisphere crop is expected to reach 28.737.570 T, which represents a decrease of slight decrease of 1 % compared to the 2019 crop. This decreased volume is the result of alternance in some countries compared to last year, as well as the impact of the droughts recorded in several production regions in the Northern Hemisphere.
By citrus categories, most categories showed decreases in production. Orange is expected to decrease by 2 %, lemon by 7 % and grapefruit by 9 %. The only category increasing production volumes compared to the previous year is soft citrus (+5 %). Looking at production by region, European production is expected to experience an increase in volume, with 12 % increases recorded for both Italy and Spain, respectively, and a 1 % decrease for Greece. In the Southern rim of the Mediterranean, crop forecasts for Egypt (-8 %), Israel (- 4 %) and Turkey (-15 %) have been lowered compared to 2019 volumes. On the other hand, Morocco and Tunisia forecast increases in their citrus crops this year, by 13 % and 20 % respectively compared to 2019 figures. On its side, the United States production is expected to decrease by 9 % compared to the precedent year, with California lowering its forecast by 5 % and Florida by 14 %.
WCO will present this forecast during the first edition of the Global Citrus Congress, which the World Citrus Organisation is co-organising with Fruitnet. The Congress with an expected attendance of more than 1.000 delegates will be the perfect opportunity to presents these latest global production figures and trade trends, as well as the importance of sustainability in citrus production and of nutrition and promotion to increase global citrus consumption.
WCO Members are ABCM- Associação Brasileira de Citrus de Mesa (Brazil), Ailimpo – Asociación Interprofesional de Limón y Pomelo (Spain), AKIB – Mediterranean Fresh Fruit and Vegetables Exporters Association (Turkey), Citrus Australia (Australia), Citrus Growers’ Association (South Africa), Chilean Citrus Committee (Chile), Fruitimpresse (Italy), Moroccan Interprofessional Citrus Federation – Maroc Citrus (Morocco), Plant Production Marketing Board (Israel), Procitrus – Asociacion de Productores de Citricos del Peru (Peru), Upefruy – Unión de Productores y Exportadores de Fruta del Uruguay (Uruguay).
WCO Associated Members are AgroFresh (Spain), AM FRESH Group (Spain), Citrusvil (Argentina), Easyfresh Logistics (Spain), FruitOne (South Africa), G.F. Marketing (South Africa), Janssen Preservation and Material Protection (Belgium), MAFA-Magrabi Agriculture (Egypt), Morocco Foodex (Morocco), Oranfrizer (Italy), PCN (USA), River Front Packing (USA), San Miguel Global (South Africa) and Zalar Agri-Agricole Centre (Morocco).
The Brazilian exports of Frozen Concentrate Orange Juice (FCOJ) Equivalent (2019/20 crop) are ending, and the volume sold to all destinations continues higher than that last season.
From July/19 to May/20, Brazil shipped 1.03 million tons of juice, 13 % more than that exported in the first 11 months of the 2018/19 season (913.4 thousand tons), according to data from Secex. Revenue, in turn, rose by 1 % (in the same comparison), totaling 1.7 billion USD.
To the European Union, specifically, Brazilian juice shipments totaled 723.7 thousand tons, 23 % up compared to that in the same period last season (587.7 thousand tons). Revenue amounted 1.2 billion USD, for an increase of 10 %. To the United States, Brazilian exports have decreased by 19 % this season, to 154.5 thousand tons, and the revenue downed 25 %, to 248.96 million USD.
Low demand explains the decrease in the volume sent to the US, due to the forecast for a recovery in the 2019/20 season in Florida for the second consecutive year. The state has faced several problems involving weather and plant health this season and in previous crops.
However, due to the covid-19 pandemic, juice sales in the American retail market have increased significantly – data from Nielsen indicate that, this season (from October/19 to April 11, 2020), the volume sold was 6.1 % higher than that in the same period of the crop before.
In this scenario, local juice stocks are being consumed. Although inventories are higher than that in the season before, projections indicating an increase in stocks are lower than those at the beginning of the year.
BRAZILIAN MARKET IN JUNE – The trading pace for citrus was weak in the first half of June, but the volume of oranges available in the in natura market was lower, since processing plants were receiving fruits in that period. Therefore, the average price for pear oranges in the first fortnight of the month was 25.25 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, 4.7 % down compared to that in the first half of May.
Players surveyed by Cepea reported higher sales of ponkan tangerine in São Paulo between June 1 and 15. Thus, the harvesting of this variety stepped up in that period, so that growers could take advantage of the high price levels, although fruits have not reached the ideal maturation stage yet.
Production in the citrus belt (São Paulo and Triângulo Mineiro) is higher in the 2019/20 season. The demand for fruits, in turn, was firm in 2019 because of low ending stocks of orange juice at processing companies from São Paulo. Therefore, higher demand and the record productivity in the field kept profitability positive. Moreover, the fact that most trades with the industry had been closed previously and at the same price levels observed on 2018/19 also favored profitability.
Fundecitrus (Citrus Defense Fund) released a report in December indicating that the orange production in the citrus belt may increase 34.7 % in 2019/20, totaling 385.31 million 40.8-kilo boxes. Productivity per hectare is likely to reach 1,041 boxes, a record. The good result is attributed to favorable weather during flower development (in the second semester of 2018) and to the fact that plants recovered after the previous lower production.
INDUSTRY – Prices for the industrial sector concerning the contracts closed in October and November 2018 ranged from 20.00 to 22.00 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, harvested and delivered at processors, similar to that in the previous crop, despite the current high supply. However, for the producers who trade with companies in the spot market, values were at 20.00 BRL per box – in the previous season, they reached 26.00 BRL per box.
However, quotes in the spot market increased in December, scenario that may be related to perspectives for lower production in the 2020/21 season. As a result, one of the major processing companies started to purchase fruits at 20.00 BRL per box from December onwards – the average price most part of the crop was 18.00 BRL per box, harvested and delivered. Another major company continued to bid 18.00 BRL per box in the last month of 2019, but the price was 16.00 BRL/box during the season.
INVENTORIES – In 2019/20, the industrial demand was firm, due to low stocks at processing companies in São Paulo, of 253.18 thousand tons of orange juice in June/19, according to CitrusBR. This volume is 26.2 % lower compared to that in the 2017/18 season.
IN NATURA MARKET – Higher orange supply pressed down quotes in the in natura market in 2019. Between July and November, the average price for pear oranges was 29 % below that in the same period of 2018, in nominal terms.
However, the 2018/19 harvest was small, pushing up quotes, which hit nominal records from July to December 2018, considering Cepea series (since 1994). Compared to quotes in the 2017/18 season, price averages between July and November 2019 were 20 % higher, in nominal terms.
EXPORTS – After a season with low shipments, orange juice trades to the international market have recovered in 2019/20. The good performance is linked to the higher production in São Paulo and the possible needs to build stocks from juice bottling companies. In the partial of the season (from June to November/19), 550.13 thousand tons of orange juice were exported to all destinations, 46 % more compared to the same period last crop.
TAHITI – The market behavior was atypical in 2019. Despite the higher production, values were high throughout the year, sustained by firm demands (domestic and international). The average from January to November was 34.58 BRL per 27-kilo box, harvested, only 4.3 % down compared to that in 2018, in nominal terms.
Brazilian exports of tahiti lime hit a record last year. The dry weather in Mexico, major competitor regarding shipments to the European Union, favored exports good performance.
The Brazilian exports of Frozen Concentrate Orange Juice (FCOJ) Equivalent in the 2018/19 season are ending and the volume shipped to all destinations is still low – May was the ninth consecutive month of lower sales (this scenario has been observed since September/18).
This scenario, which was already expected by agents, is linked to the lower orange production in the Brazilian citrus belt (São Paulo and Triângulo Mineiro) this season as well as lower demand from the international market, mainly the United States. The exports decrease, in turn, prevents orange inventories of Brazilian processing plants from decreasing to critical levels by the end of the season (June 30 2019).
This season (July/18 to May/19), Brazilian juice exports to all destinations have decreased 18 % compared to the same period in the 2017/18 season, totaling 918.46 thousand tons, according to Secex. Revenue, in turn, has dropped 17%, totaling 1.69 billion USD.
Exports to the European Union, the biggest purchaser of the Brazilian juice, totaled 592 thousand tons, 8 % down compared to that in the same period last year. Revenue, in turn, totaled 1.09 billion USD, 6 % down in the same comparison.
Shipments to the United States had the steepest decrease in the season, of 38 % compared to the previous crop, totaling 190.71 thousand tons of juice. This result is linked to the lower demand from the USA, due to the estimates for the recovery of the 2018/19 crop from Florida as well as lower consumption. Revenue, in turn, dropped 39 % in the same comparison, totaling 331.55 million USD.
ESTIMATES – According to a report released by the USDA on June 11, the orange crop from Florida should increase by 58.4 % compared to the previous, totaling 71.4 million boxes (1.3 % down compared to that forecast in May).
Despite the decrease in the consumption of orange juice in the United States, the demand from the country for the Brazilian orange juice may not decrease too sharply in the coming seasons, due to the effects of greening on American crops in the long term.
BRAZILIAN MARKET – The trading pace was slow in the Brazilian citrus market in the first fortnight of June. However, the volume of oranges in the ideal stage for the in natura market was gradually decreasing in São Paulo, due to the increase in the deliveries to processing plants. Thus, between June 3 and 14, pear orange quotes averaged 18.08 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, on tree, 21.5 % down compared to that in the first half of May.
As for tahiti lime, despite the large volume available for harvesting, the current weather allows the fruits to stay on tree for longer. Thus, growers reduced the pace of activities in the field, aiming to prevent prices from dropping too much. In the first half of June, tahiti lime quotes averaged 13.65 BRL per 27-kilo box, harvested, a slight 20.6 % down compared to that in the first fortnight of May.
EXPORTS – Lemon and lime shipments were positive in May, surpassing, for the first time in the year, the amount exported in 2018. Last month, exports hit a record (revenue and volume) in all Secex series, which started in 1997.
According to Brazilian exporters consulted by Cepea, as the weather delayed the maturation of tahiti lime crops in SP, shipments decreased from March to April, increasing again in May. According to data from Secex, Brazil exported 18.94 thousand tons of lemon and lime in May, almost two-fold the amount shipped in May 2018 and 57% more than that exported in April/19.
Florida Orange and Grapefruit production both decreased by 500,000 boxes in the April U.S. Department of Agriculture crop forecast.
The report projects Florida Orange production for the 2018-19 season at 76.5 million boxes after a slight decline in Non-Valencia orange production. Florida Grapefruit production is now estimated at 4.9 million boxes.
“We’re an industry catching glimpses of recovery, but this estimate certainly points out that we are not there yet,” said Shannon Shepp, executive director of the Florida Department of Citrus. “It’s still a great year, but we are anxious for better.”
The numbers remain an increase from the previous season, devastated by Hurricane Irma, when production dropped to 45.05 million boxes of Florida Oranges and 3.88 million boxes of Florida Grapefruit.
The first oranges from the 2019/20 season started to arrive at the market of São Paulo State in the first fortnight of March. Despite the small volumes harvested, trades started in the same month as production did last year. Thus, Brazilian citrus growers believe the output of early oranges will be able to supply the Brazilian in natura market.
Considering the favorable weather during the development of the flowers of these varieties (second semester of 2018), the citrus growers consulted by Cepea have reported a satisfactory flower settlement –, resulting in a positive volume harvested in all producing regions this new season. For now, supply has been controlled, due to the delay in fruits growth, which, in turn, reflects the lack of rains in January. In this scenario, most early oranges have not reached the ideal maturation stage for the in natura segment yet.
According to growers, among the fruits supplied in the first fortnight of March, the main varieties were rubi, hamlin and lima sorocaba – traded at 30 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, on average, on tree. The remaining varieties, such as westin and baía, may arrive at the market starting the second half of the month, as they reach the ideal stage.
However, supply should not be large enough to lead too many processors to start activities. Thus, until mid-April, the main destination of these fruits should be the in natura market – mainly to offset the low supply of pear oranges in the offseason period.
BRAZILIAN MARKET – The Carnival period in Brazil (March 2 to 6) weakened the demand for oranges in early March. Supply, in turn, was limited by the rains in São Paulo, which lowered fruits quality, mainly for late oranges. The growers consulted by Cepea reported the harvesting end for pear and late oranges.
Thus, between March 1 and 15, pear orange quotes averaged 43.32 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, on tree, 15.1% up compared to that in the first fortnight of February.
The smaller volume of oranges allocated to processors in the 2016/17 season (due to one of the smallest crops in the citrus belt, with only 245.3 million boxes of 40.8 kilos) has affected not only orange juice exportations, but shipments of orange by-products as well. While in the 2015/16 season exportations of these products increased, shipments of all items from the crop that officially ended in June (July/16 to June/17) had the worst individual performance, mainly in terms of volume.
The revenue from by-products exportations in the 2016/17 season, however, was 390.08 million USD, 22 % up compared to the previous crop (Secex). Except for lemon and lime oil, prices of all the other by-products increased significantly in the season. These exportations include citrus pulp pellets, citrus terpenic, D-limonene, lemon, lime and orange essential oils and other citrus products.
As for the individual performance, only two by-products had higher shipments compared to the previous season: D-limonene and lemon essential oil. On the other hand, the volume of citrus pulp pellets exported decreased a staggering 68 %, totaling 68.6 thousand tons.
FCOJ – Exportations of frozen concentrate orange juice equivalent (FCOJ Equivalent) decreased 17 % compared to the previous crop. From July/16 to June/17, exportations of FCOJ Equivalent totaled 950.92 thousand tons, according to Secex. Revenue totaled 1.73 billion USD, 6 % down compared to the same period last crop. In Real, revenue totaled 5.57 billion BRL, 18 % down in the same comparison.
Brazilian exportations should increase next season, based on the partial recovery of the orange juice inventories.
BRAZILIAN MARKET – Demand for in natura oranges weakened in the second week of July, due to the mild temperatures in São Paulo State and the school vacations period. Thus, pear orange quotes averaged 16.30 BRL per 40.8-kilo box (on tree) between July 3 and 14, 7.1 % down compared to the same period in June.
Purchases from processors were limited as well. Receiving previously purchased fruits, processors from SP State did not trade much in the spot in the first fortnight of July, mainly due to maturation out of the ideal period for some fruits, mainly the mid-season ones. Thus, bidding prices continued between 16.00 BRL and 18.00 BRL per 40.8-kilo box, harvested and delivered at the processor, and between 18.00 BRL and 20.00 BRL per box for the mid-season fruits.










 Due to the flowering in non-traditional months (December and January) there are a large number of “green”, not yet ripe fruits mixed with ripe fruits from the normal flowering (August-September 2019). This brings an additional difficulty to the harvesting operation that has to be carried out in at least two different times, resulting in an increase of the production cost for the citrus growers.
Due to the flowering in non-traditional months (December and January) there are a large number of “green”, not yet ripe fruits mixed with ripe fruits from the normal flowering (August-September 2019). This brings an additional difficulty to the harvesting operation that has to be carried out in at least two different times, resulting in an increase of the production cost for the citrus growers.